Sleep Facts
Some 70 million people in the US have a sleep problem. About 40 million adults suffer from a chronic sleep disorder; an additional 20-30 million have intermittent sleep-related problems.
Effects of sleep loss on work performance may be costing US employers some $18 billion in lost productivity.
America's adults average 6.9 hours of sleep each night, slightly less than the range of 7-9 hours recommended by many sleep experts.
Three-quarters of America's adults (75%) said they frequently experienced at least one symptom of a sleep problem in the past year.
More than 3/4 of America's partnered adults (77%) say their partner nas a sleep-related problem; the most common problem is snoring.
One-quarter of America's adults, 47 million people, don't get the minimum amount of sleep they say they need to be alert the next day.
People who are already hypertensive may increase their risk of heart attack or stroke if they fail to get adequate sleep.
Shift workers are 30%-50% more likely to develop heart disease than day workers in the same industry.
More than 1/2 of America's adults nap at least once a week.
While the majority of America's adults do not use anything to help them sleep, for those who do use a sleep aid, alcohol appears to be the most popular choice; 11% of adults said they used alcohol, beer, or wine at least a few nights a month, 9% used over-the-counter sleep aids, 7% said they used prescription sleep medications.
About 6 in 10 adults licensed to drive (60%), or about 118 million people, said they have driven drowsy at least once in the past year.
17%, 32 million people, said they fell asleep at the wheel.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, at least 100,000 police-reported crashes are caused by drowsy drivers each year. These crashes result in more than 1,500 deaths and 71,000 injuries.

Healthy Sleep Habits
 Get up at the same time every day.
Get up at the same time every day.
 Try to sleep only when drowsy.
Try to sleep only when drowsy.
 Maintain a relaxing pre-sleep routine. This may include a warm bath (1-2 hours before bedtime), relaxation exercises, or quiet reading.
Maintain a relaxing pre-sleep routine. This may include a warm bath (1-2 hours before bedtime), relaxation exercises, or quiet reading.
 Keep the bedroom dark, cool, and quiet while sleeping.
Keep the bedroom dark, cool, and quiet while sleeping.
 If you are unable to fall asleep or stay asleep, get out of bed and engage in quiet activity such as reading. Return to bed only when sleepy.
If you are unable to fall asleep or stay asleep, get out of bed and engage in quiet activity such as reading. Return to bed only when sleepy.
 Exercise regularly, but do not exercise vigorously within several hours of bedtime.
Exercise regularly, but do not exercise vigorously within several hours of bedtime.
 Keep a consistent daily schedule for meals, medication, and other activities.
Keep a consistent daily schedule for meals, medication, and other activities.
 Long naps can disturb your nighttime sleep. If necessary, 20-30 minute naps in the early afternoon are best.
Long naps can disturb your nighttime sleep. If necessary, 20-30 minute naps in the early afternoon are best.
 Avoid caffeine and alcohol within 4 hours of bedtime.
Avoid caffeine and alcohol within 4 hours of bedtime.
 Avoid nicotine near bedtime.
Avoid nicotine near bedtime.

Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Sleep apnea affects some 18 million people. According to National Sleep Foundation's 2002 Sleep in America poll, about 1 in 10 adults reported experiencing some pauses in breathing during sleep. Snoring can be a symptom of sleep apnea. About 59% of adults said they snore, according to the same poll. About 1/4 of those who snore do so every night or almost every night. In sleep apnea, the airway of the snorer closes and he/she must wake up to resume breathing. This cycle may repeat hundreds of times during the night, resulting in severe daytime sleepiness.
What are the risks to my health from Sleep Apnea?
 High Blood Pressure
High Blood Pressure
 Stroke
Stroke
 Heart Attack
Heart Attack
 People with untreated sleep apnea are 2-7 times more likely to have automobile crashes than the general population.
People with untreated sleep apnea are 2-7 times more likely to have automobile crashes than the general population.
What are some of the signs of Sleep Apnea?
 Loud Snoring
Loud Snoring
 Snoring accompanied by snorts, gasping or choking noises
Snoring accompanied by snorts, gasping or choking noises
 Snoring with pauses
Snoring with pauses
 Daytime Sleepiness
Daytime Sleepiness
 Changes in alertness, memory and interest in daily activities
Changes in alertness, memory and interest in daily activities
 Irritability and/or Depression
Irritability and/or Depression
 High blood pressure (when found in combination with the above symptoms)
High blood pressure (when found in combination with the above symptoms)
 Accidents or near misses related to sleepiness
Accidents or near misses related to sleepiness
Who is at risk for having Sleep Apnea?
 Males: twice as likely as females
Males: twice as likely as females
 Primarily men and women in the 30-50 age bracket
Primarily men and women in the 30-50 age bracket
 Obese individuals or those more than 20% over their ideal weight
Obese individuals or those more than 20% over their ideal weight
 Individuals with difficulty breathing through their noses
Individuals with difficulty breathing through their noses
 Children or adults with enlarged tonsils
Children or adults with enlarged tonsils
 Children who are obese
Children who are obese
Is there anything I can try to help with my snoring?
 Lose Weight
Lose Weight
 Drink only in moderation and avoid alcohol within two hours of bedtime
Drink only in moderation and avoid alcohol within two hours of bedtime
 Avoid sleeping pills and other medications, which make you sleepy
Avoid sleeping pills and other medications, which make you sleepy
 Sleep on your side
Sleep on your side
 Treat nasal congestion. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for their recommendations
Treat nasal congestion. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for their recommendations
 Avoid extreme fatigue
Avoid extreme fatigue
 Stop smoking
Stop smoking
How is Sleep Apnea diagnosed?
The diagnosis of this disorder requires an overnight sleep study.
How is Sleep Apnea treated?
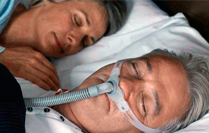
 CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): In this highly effective therapy, a mask is worn over the nose during sleep. Pressure from an air compressor enters the nasal passages and airway. This gentle pressure holds the airway open and allows the person to breathe normally.
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): In this highly effective therapy, a mask is worn over the nose during sleep. Pressure from an air compressor enters the nasal passages and airway. This gentle pressure holds the airway open and allows the person to breathe normally.
 Oral Appliances: Devices that may help some apnea patients are designed to open the airway by bringing the jaw, tongue and soft palate forward.
Oral Appliances: Devices that may help some apnea patients are designed to open the airway by bringing the jaw, tongue and soft palate forward.
 Surgery: There are surgical procedures designed to correct abnormalities of the upper airway. These abnormalities may include enlarged tonsils or adenoids, nasal polyps or other growths, a deviated nasal septum and malformations of the jaw or soft palate. In one common procedure excess tissue at the back of the throat may be removed. An evaluation by an Ear, Nose and Throat specialist is necessary to determine if you are a candidate for any of these surgical procedures.
Surgery: There are surgical procedures designed to correct abnormalities of the upper airway. These abnormalities may include enlarged tonsils or adenoids, nasal polyps or other growths, a deviated nasal septum and malformations of the jaw or soft palate. In one common procedure excess tissue at the back of the throat may be removed. An evaluation by an Ear, Nose and Throat specialist is necessary to determine if you are a candidate for any of these surgical procedures.
 Oxygen: This is rarely needed for the treatment of Sleep Apnea alone. Oxygen, however, may be added to the nasal CPAP system to correct for low oxygen levels due to existing lung or heart disease.
Oxygen: This is rarely needed for the treatment of Sleep Apnea alone. Oxygen, however, may be added to the nasal CPAP system to correct for low oxygen levels due to existing lung or heart disease.
 Medication: This is generally of limited benefit for sleep apnea sufferers.
Medication: This is generally of limited benefit for sleep apnea sufferers.
The suggestions above for treatment of snoring also pertain to people with Sleep Apnea.
Always follow rules of Good Sleep Hygiene.
A.W.A.K.E. — Awake, Alert and Keeping Energetic (OSA support group)
Visit the American Sleep Apnea Association website for more information and educational resources on sleep apnea.

Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy can be defined as excessive drowsiness during the day with a tendency to sleep at inappropriate times. The sleep episodes of narcolepsy are sometimes brought on by highly stressful situations and are not completely relieved by any amount of sleep.
Narcolepsy affects about one in every 2,000 people, or more than 135,000 Americans. It usually strikes people in their mid-teens to age 25.
What are the symptoms of Narcolepsy?
The four main symptoms are:
 Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
 Cataplexy - sudden, brief loss of muscle control, usually triggered by a strong emotion such as laughter, anger or surprise.
Cataplexy - sudden, brief loss of muscle control, usually triggered by a strong emotion such as laughter, anger or surprise.
 Sleep Paralysis - brief loss of muscle control that occurs when a person is falling asleep or waking up.
Sleep Paralysis - brief loss of muscle control that occurs when a person is falling asleep or waking up.
 Hypnagogic Hallucinations - vivid dreamlike experiences that occur when a person is drowsy.
Hypnagogic Hallucinations - vivid dreamlike experiences that occur when a person is drowsy.
How is Narcolepsy diagnosed?
Diagnosis of this disorder requires an overnight sleep study and a daytime nap study.
How is Narcolepsy treated?
Medication - prescription medications can be effective in controlling excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy.

Insomnia
Insomnia (trouble either falling asleep or staying asleep) is the most common sleep problem for America's adults, according to National Sleep Foundation polls. More than 1/2 of adults in America (54%) said they experienced at least one symptom of insomnia a few nights per week; 1/3 (33%) reported having a symptom every night or almost every night in the past year. Insomnia can last for only one night, a few weeks or may be a chronic problem.
What causes Insomnia?
Psychological Factors: Stress can cause insomnia. Identifying the cause and learning how to relax, in spite of the problems causing stress, can help, even if the actual cause still persists. Early morning awakenings are one of the symptoms of depression. Treatment of depression or other psychological problems can improve sleep.
Stimulants: Caffeine and Nicotine, even if they do not prevent you from falling asleep, can disrupt sleep and affect sleep quality. Medications also interrupt sleep onset and the overall quality of sleep. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about the medications you take.
Alcohol: This may make you sleepy, but can disrupt the sleep that follows. People who snore loudly may develop Sleep Apnea with alcohol.
Erratic Hours: Staying up late and sleeping in on weekends, as well as working shifts can disrupt sleep. Regular bed and wake times promote better sleep.
Inactivity: People who are fit sleep better than people who do not exercise. Exercise during the day improves sleep at night.
Learned Behaviors: Staying in bed, tossing and turning or watching the clock when you can't sleep, just makes you anxious.
Environmental Factors: Make sure your room is dark, cool and quiet.
Medical conditions that may cause sleep disruption
Breathing Problems: Some loud snorers may stop breathing during sleep. This is called Sleep Apnea. These disturbances can cause difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Restless Legs Syndrome and Periodic Limb Movements: In some people, restlessness or periodic leg or arm twitching can occur during the night and cause sleep disruption and frequent awakenings.
Gastroesophageal Reflux: Many people experience heartburn or the backing up of stomach contents into the throat. When this occurs during sleep it can cause awakenings. Elevating the head of the bed can help prevent this.
Pain: People who experience pain, either acutely or chronically, may have difficulty sleeping. Making sure your bed is comfortable and following the guidelines for Good Sleep Hygiene can help.

Restless Legs Syndrome
People experience restless legs in different ways, but all describe a very unpleasant "creepy, crawly" sensation that occurs in the legs when they are sitting or lying still, especially at bedtime. It is also different from the feeling of a limb having "fallen asleep" when the blood supply is cut off and from the "pins and needles" or burning sensation sometimes experienced by diabetics. The pain and unpleasant feelings of RLS appear most often in the calves and can be temporarily relieved by stretching and moving the legs.
If you suffer from RLS, you will find that it occurs primarily when you are awake, but that it can also affect your ability to sleep. It is estimated that RLS affects as many as 12 million Americans, though some researchers estimate a higher occurrence because RLS is thought to be under-diagnosed.
How is RLS diagnosed?
RLS has such unique symptoms that a diagnosis can often be made on the basis of a patient’s descriptions of their symptoms. A medical history and physical examination need to be obtained in order to exclude other problems.
How is RLS treated?
 Home remedies are effective for some people. These include a hot bath, leg massage, use of a heating pad, ice packs, aspirin or other pain relievers, regular exercise and elimination of caffeine.
Home remedies are effective for some people. These include a hot bath, leg massage, use of a heating pad, ice packs, aspirin or other pain relievers, regular exercise and elimination of caffeine.
 Prescription medications may help depending on the severity of the condition, other medical problems or other medications that the patient is taking.
Prescription medications may help depending on the severity of the condition, other medical problems or other medications that the patient is taking.
Periodic Limb Movement Disorder (PLMD)
People with periodic limb movements are often not aware of these movements, although they may occasionally notice the involuntary movements of PLMD while they are awake. Most people with RLS have periodic limb movements, but patients with PLMD often do not necessarily have RLS. Periodic Limb Movement Disorder may cause difficulty staying asleep at night, thus causing daytime sleepiness. They are not the same as the occasional jerks that can occur just as a person falls asleep.
How is PLMD diagnosed?
This disorder may require an overnight sleep study for diagnosis. .
How is PLMD treated?
 Follow rules of Good Sleep Hygiene.
Follow rules of Good Sleep Hygiene.
 Prescription medication may be effective.
Prescription medication may be effective.
Meet your Technician
Find a Patient Technician.